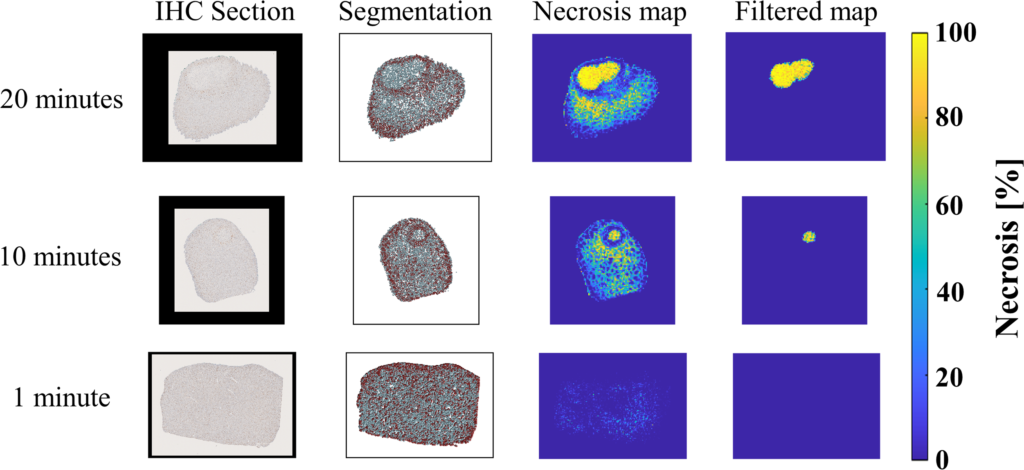
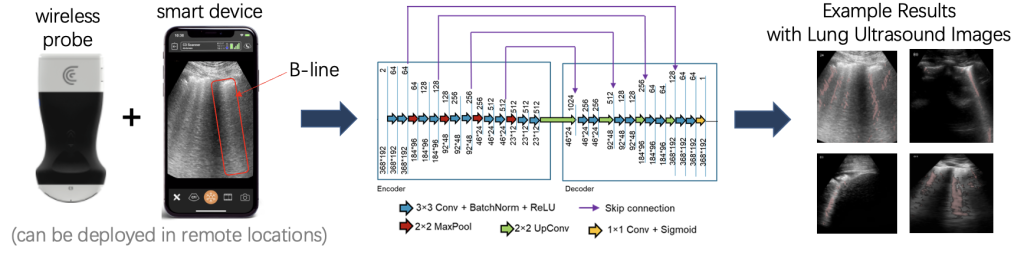
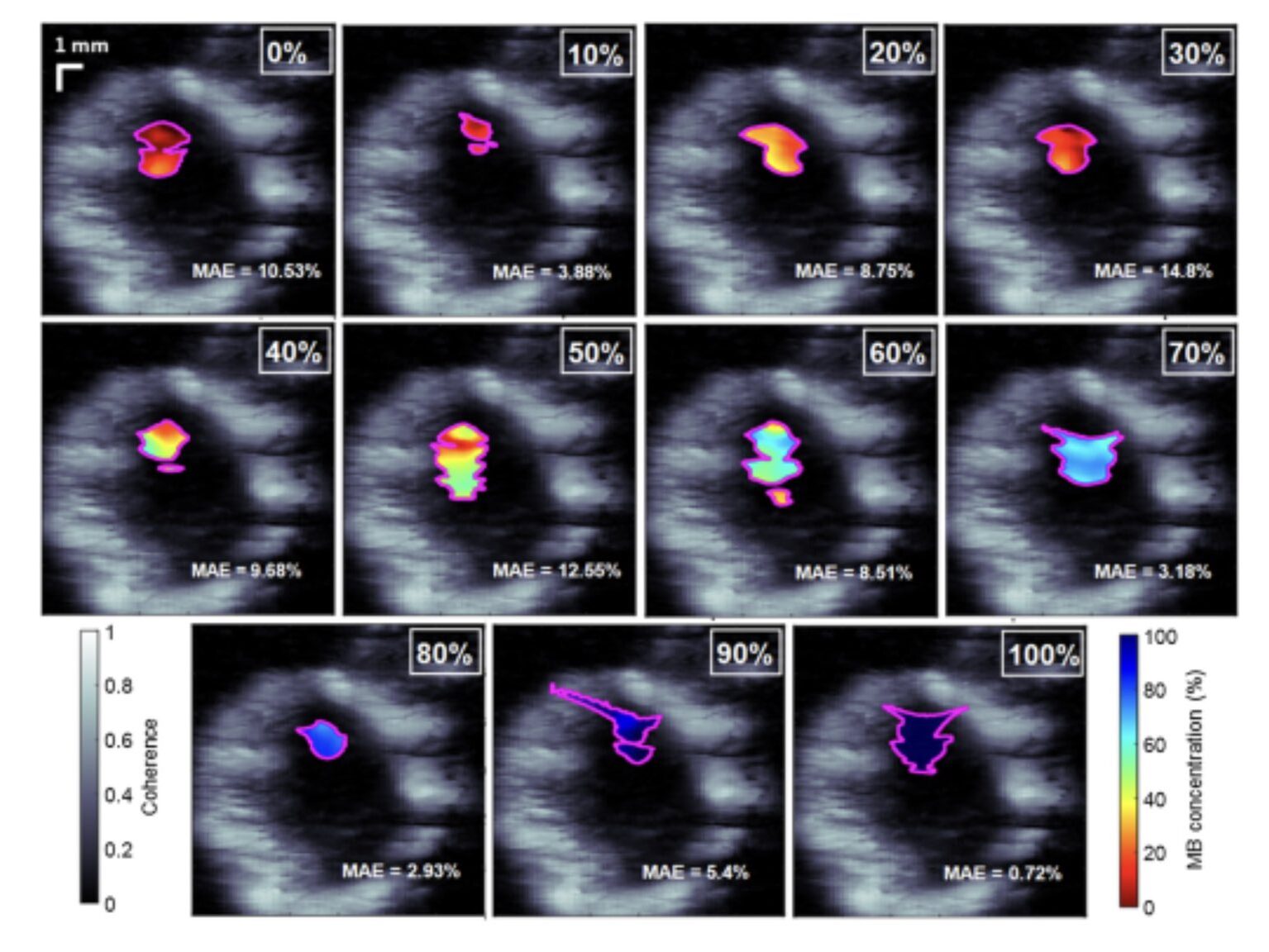
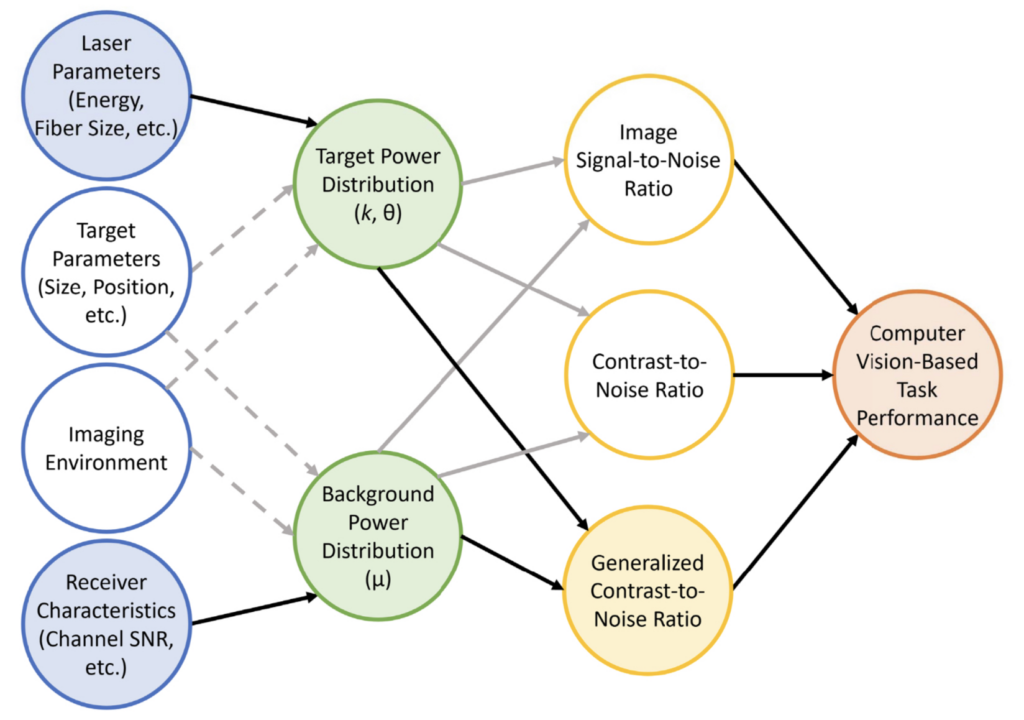
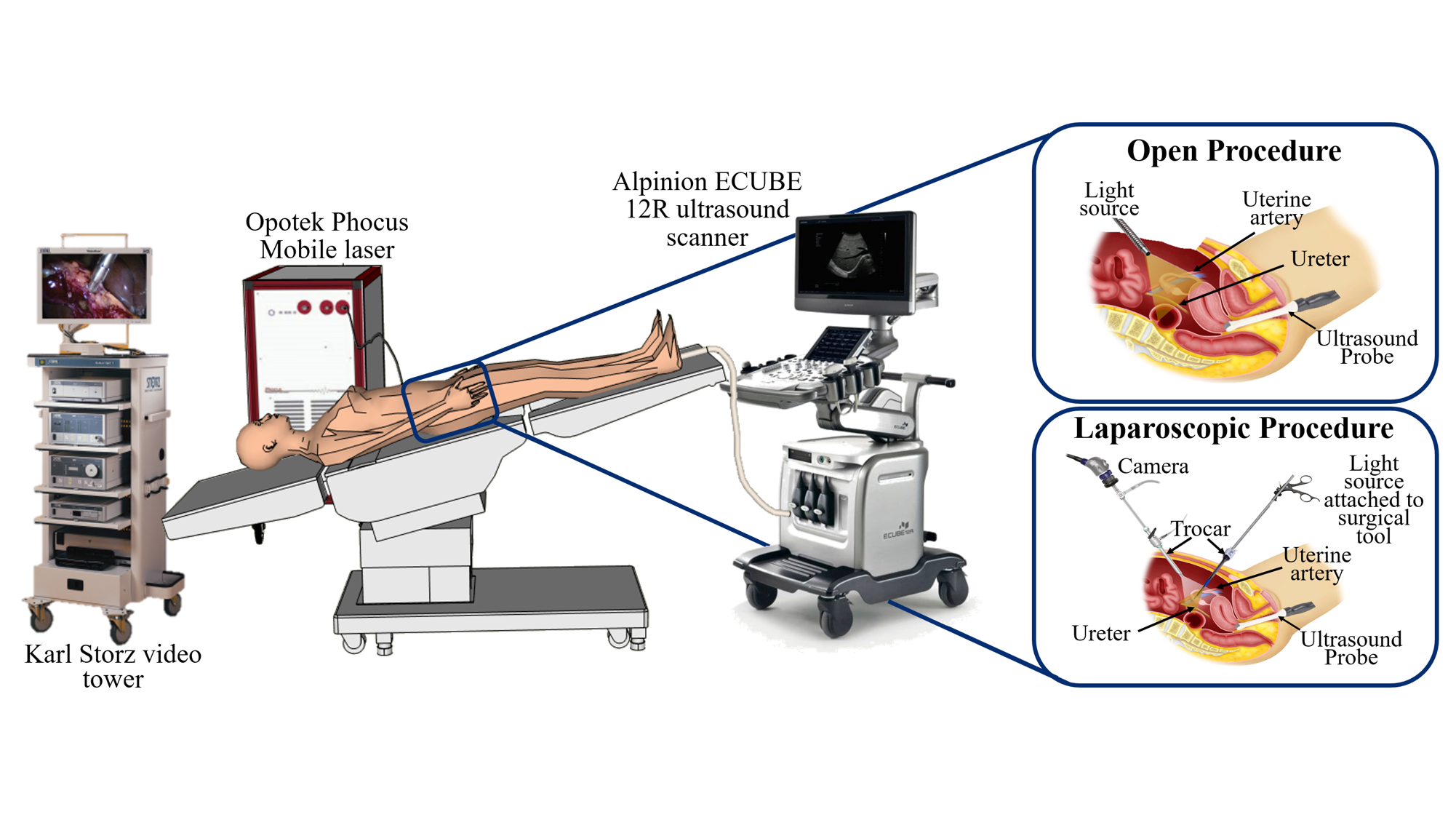
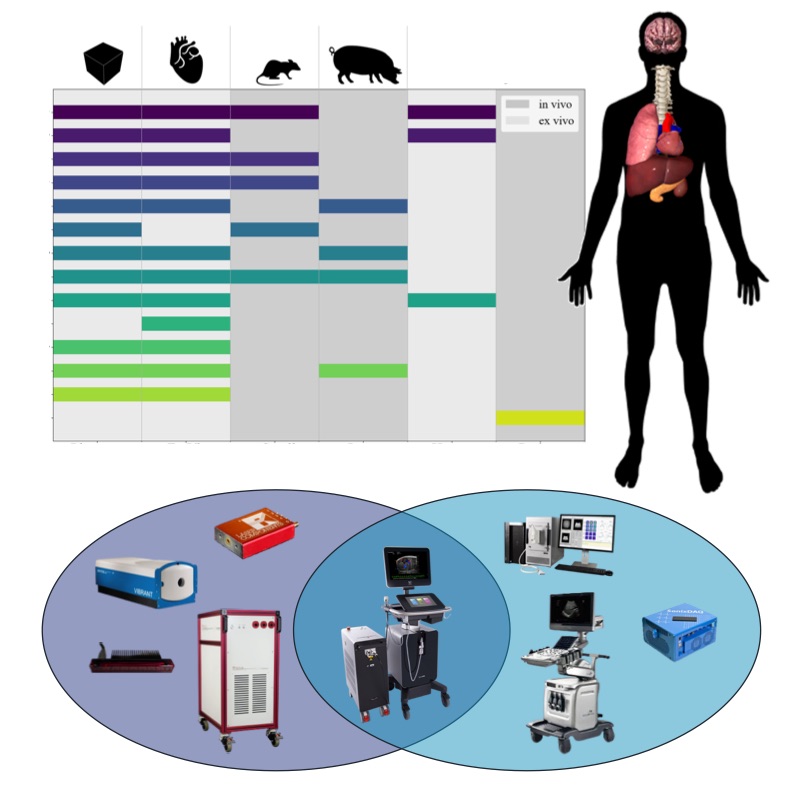
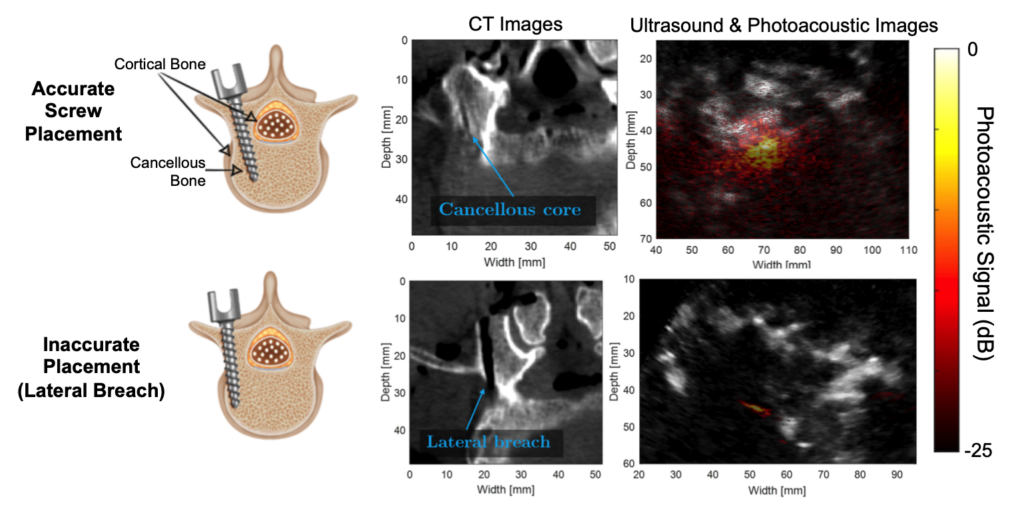
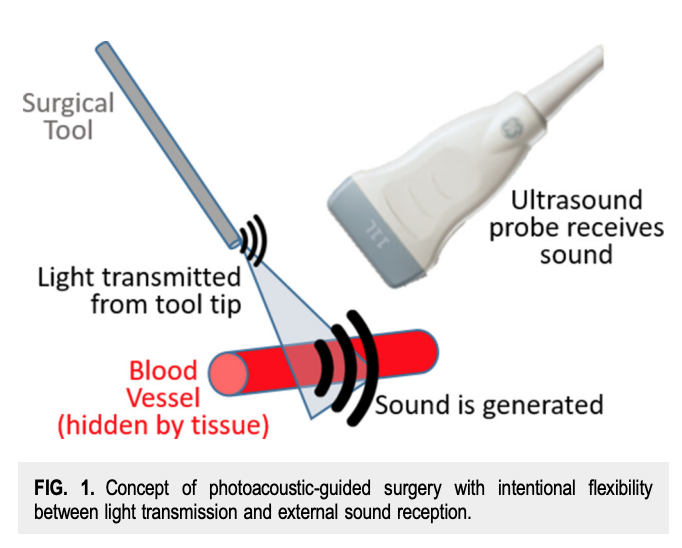
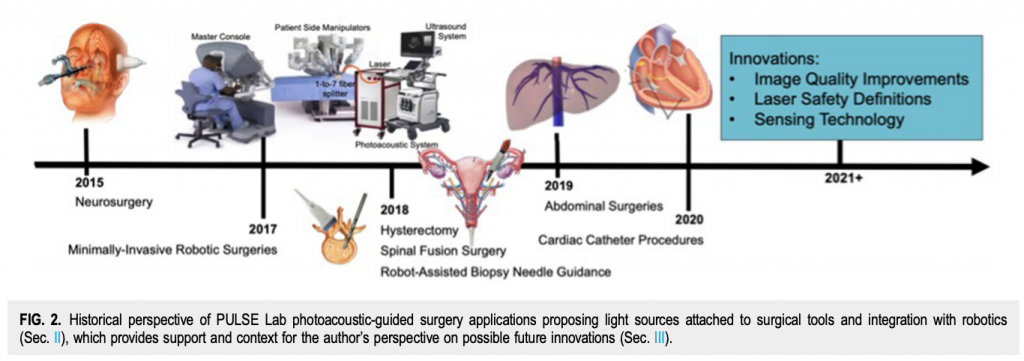
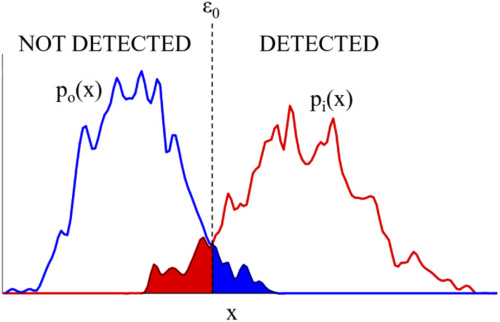
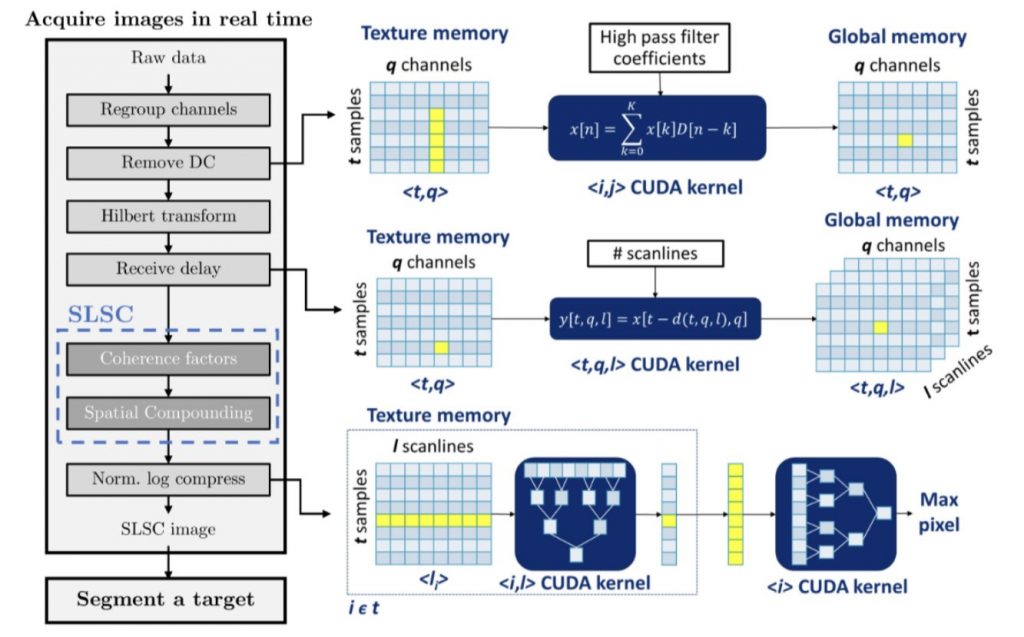
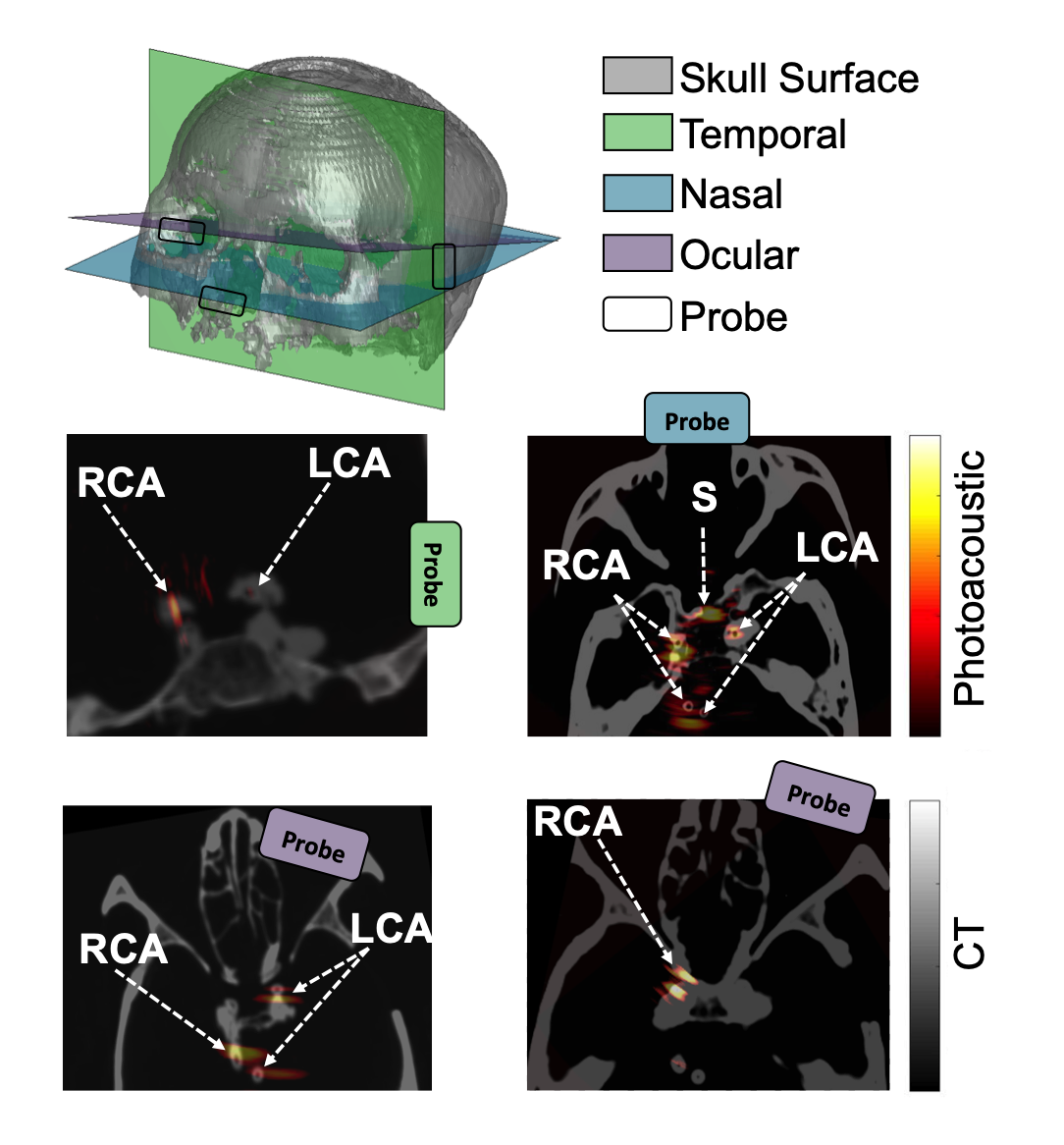
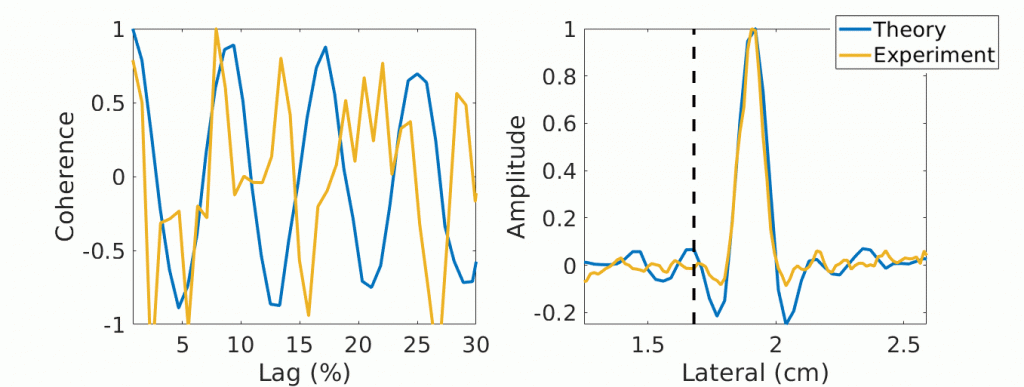
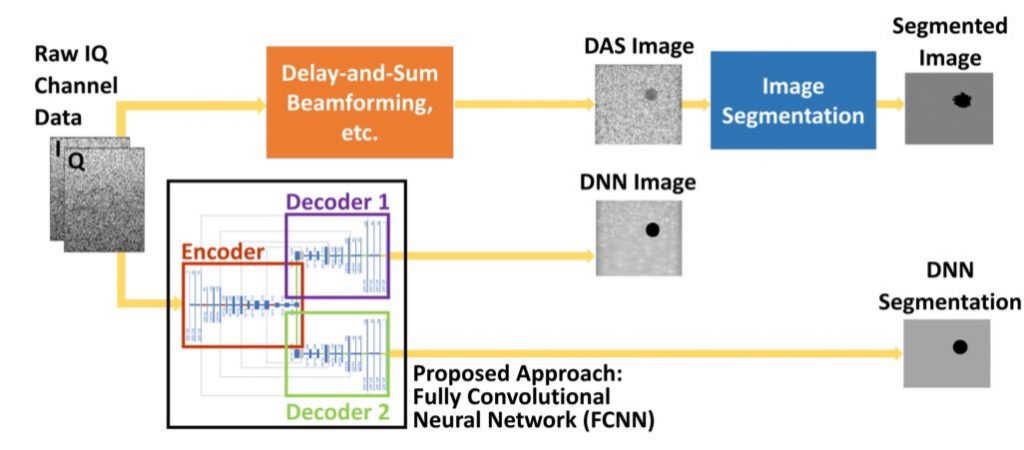
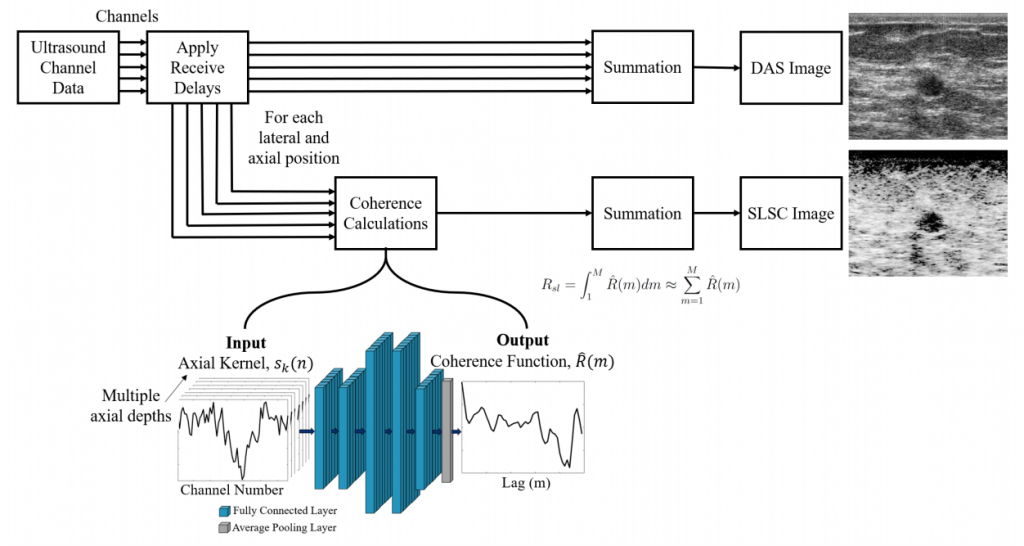
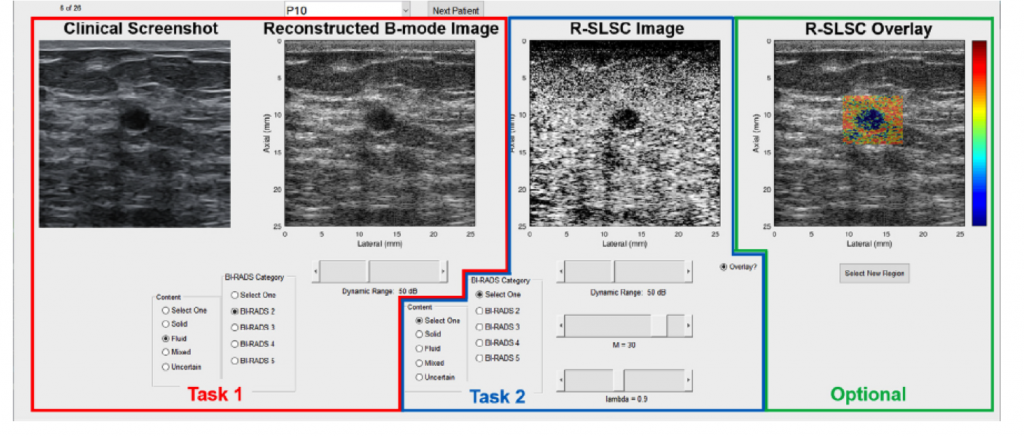
 Congratulations to Mardava Gubbi! His first-author paper entitled “In Vivo Demonstration of Deep Learning-Based Photoacoustic Visual Servoing System” was accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.
Congratulations to Mardava Gubbi! His first-author paper entitled “In Vivo Demonstration of Deep Learning-Based Photoacoustic Visual Servoing System” was accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.
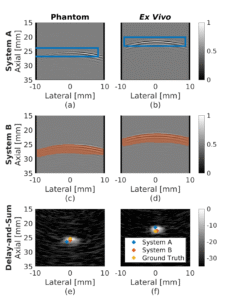
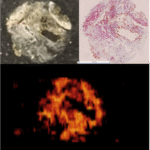
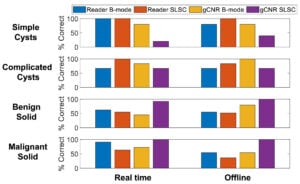
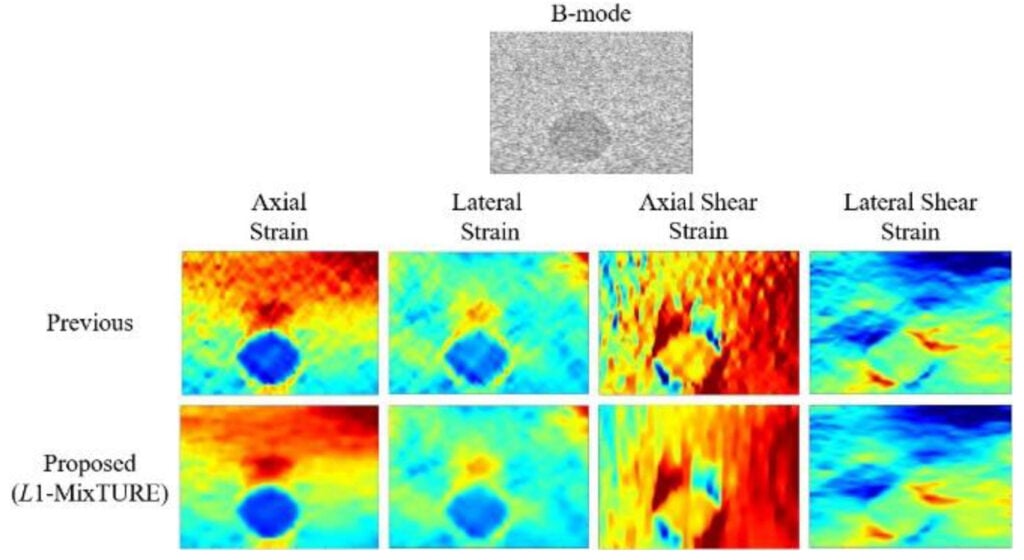
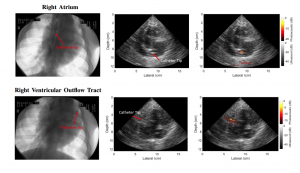
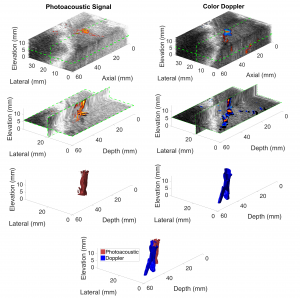
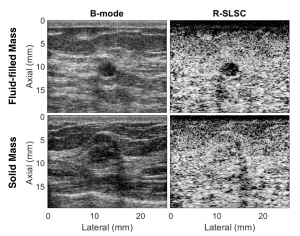
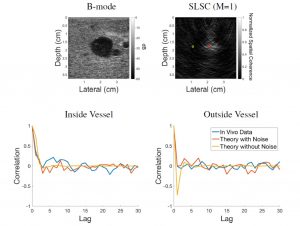
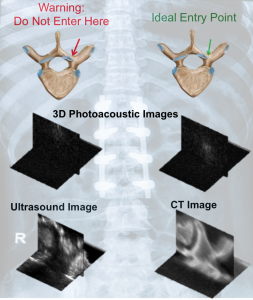
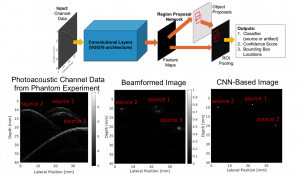
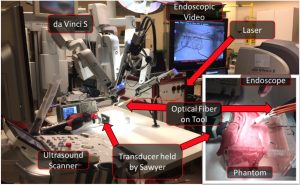
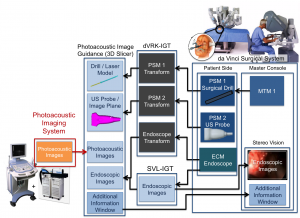
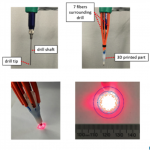
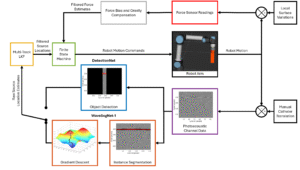
This paper is the first to present a real-time deep learning-based photoacoustic visual servoing system utilizing both object detection and instance segmentation to estimate catheter tip positions in three spatial dimensions from a single frame of two-dimensional of raw photoacoustic channel data. This system was designed with two features not present in previous amplitude-based or deep learning-based photoacoustic visual servoing systems. First, we estimated the location of the catheter tip along the elevation dimension of the transducer with the input being a single frame of two-dimensional of raw channel data. Second, the integration of force control into our visual servoing system improved the tracking of targets across uneven imaging surfaces. These features improve the potential of our novel visual servoing system for clinical translation in cardiac catheterizations procedures (and other minimally invasive interventional procedures).
Citation: M. R. Gubbi, A. Kolandaivelu, N. Venkatayogi, J. Zhang, P. Warbal, G. C. Keene, M. Khairalseed, J. Chrispin, and M. A. Lediju Bell, “In Vivo Demonstration of Deep Learning-Based Photoacoustic Visual Servoing System”, IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control (accepted June 23, 2025) [pdf]