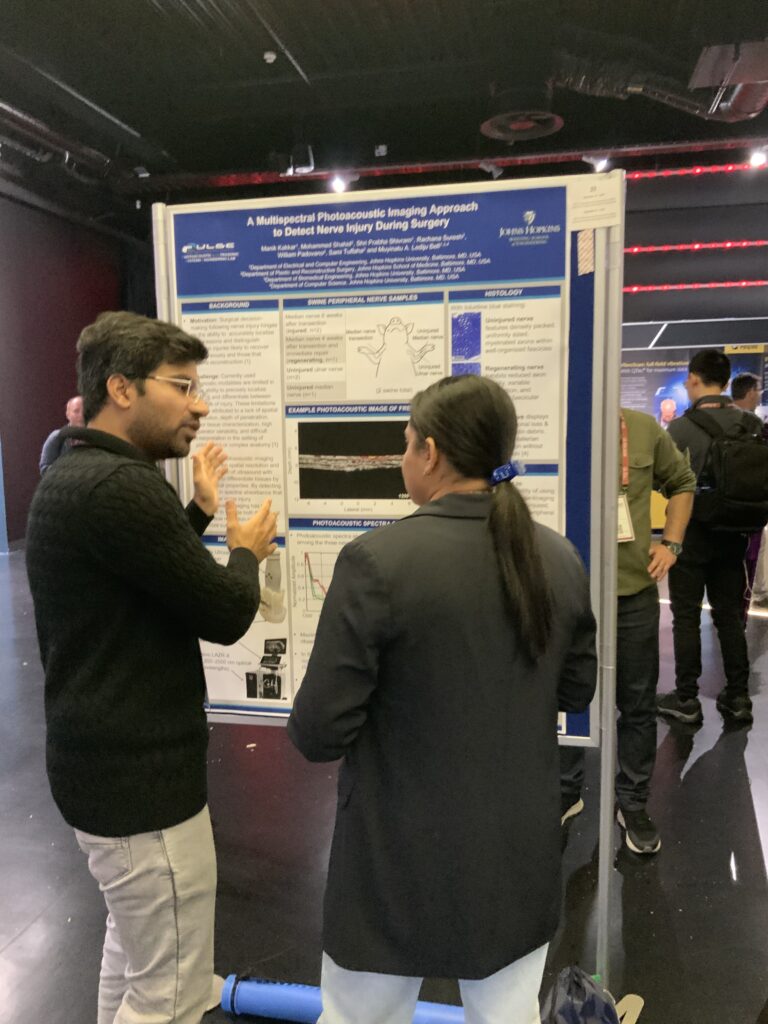
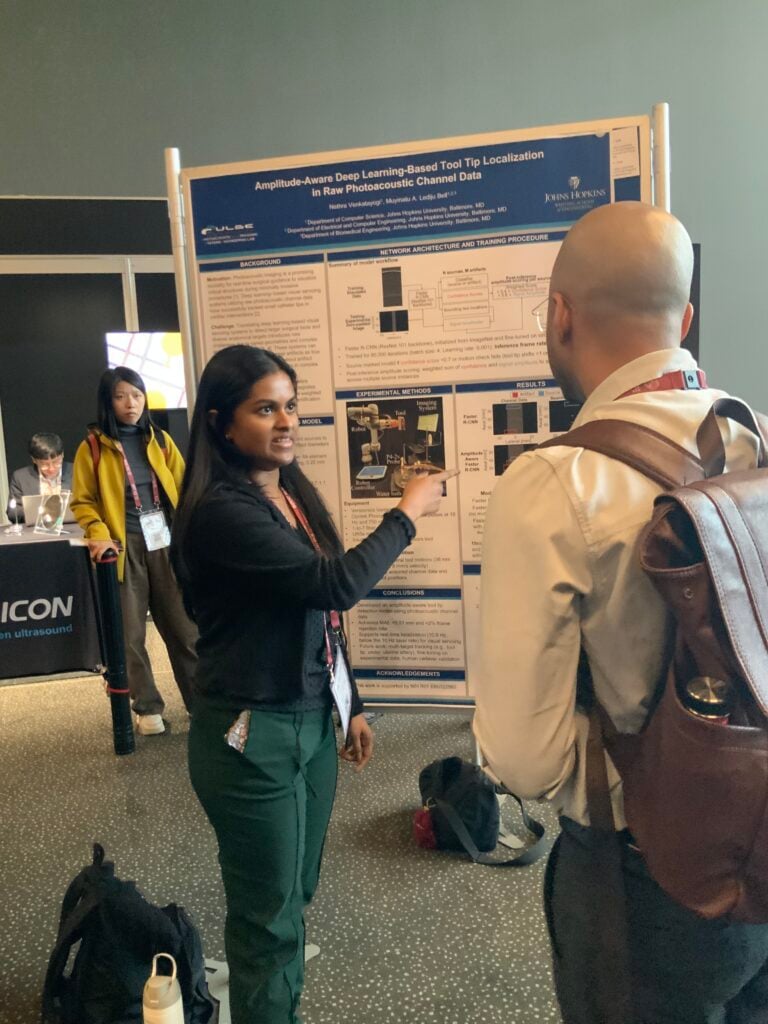
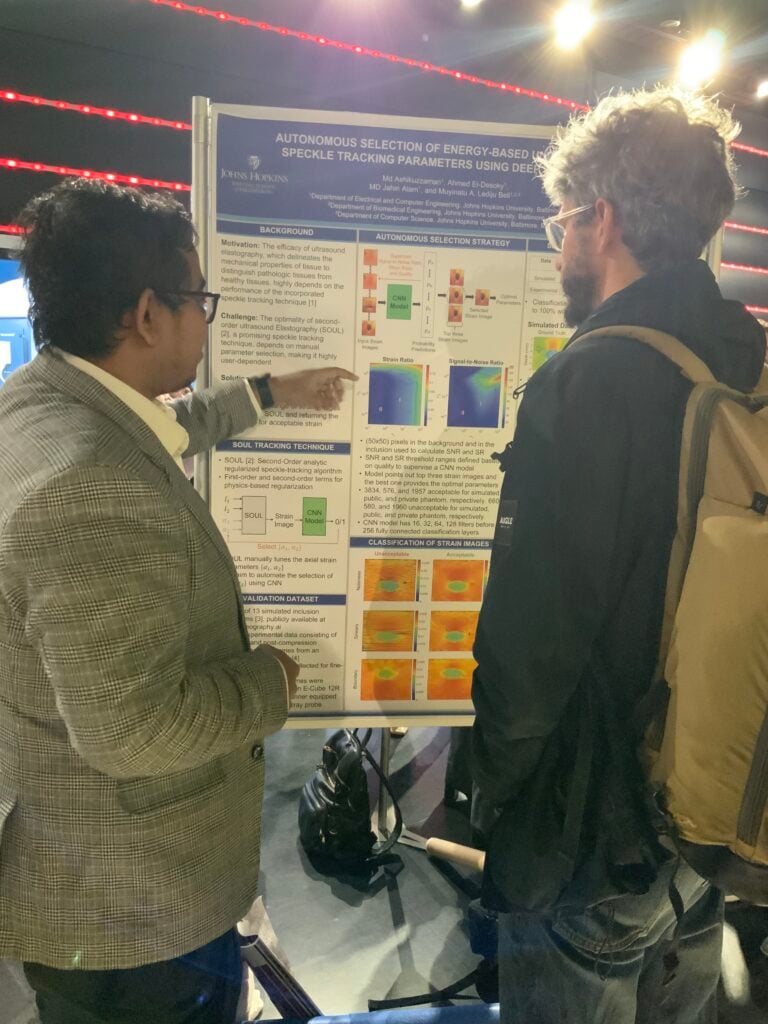
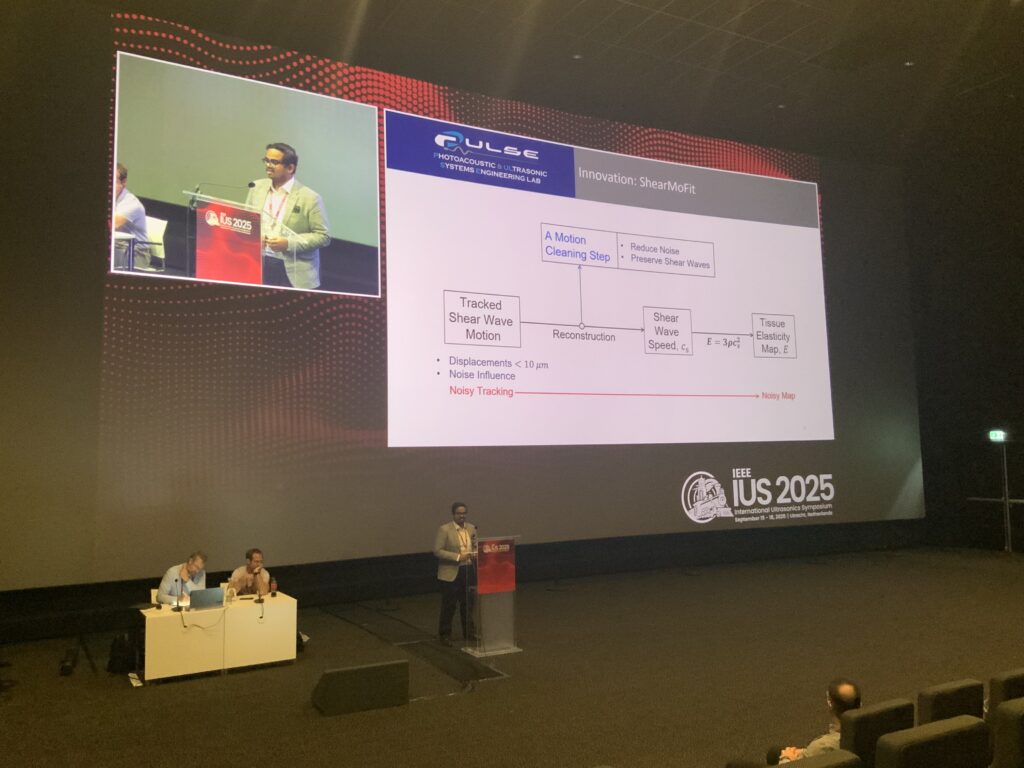
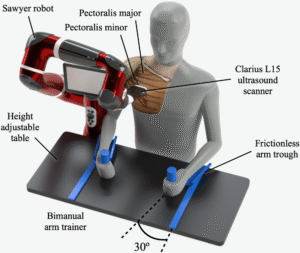
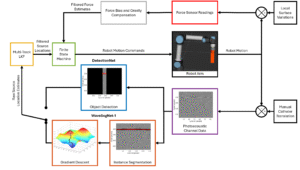
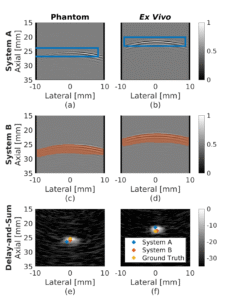
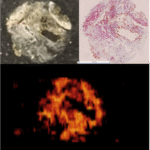
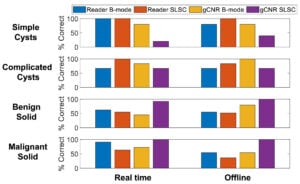
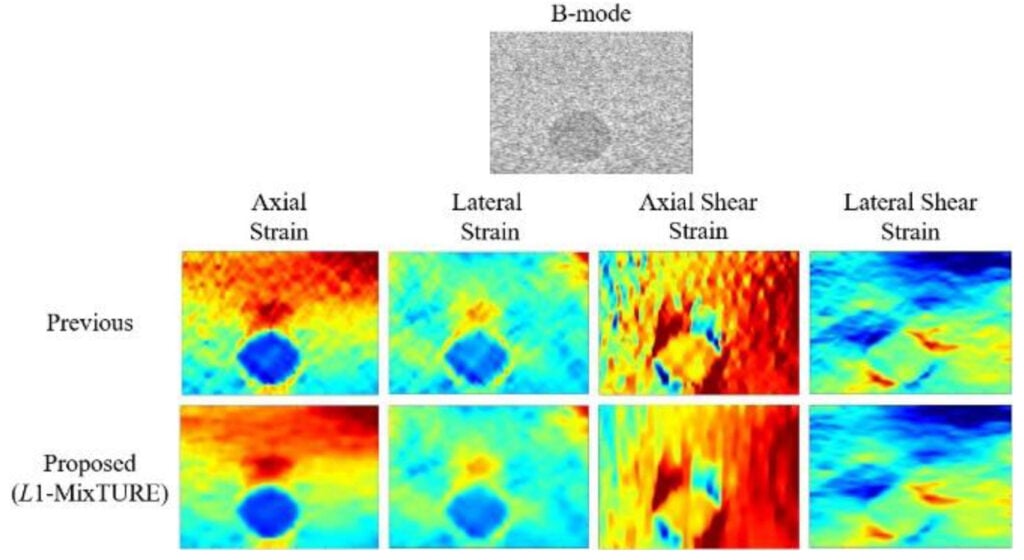
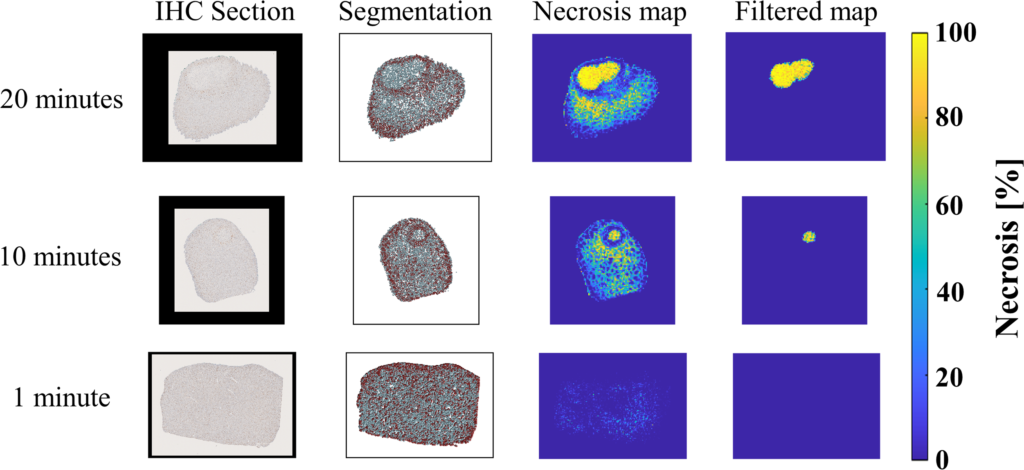
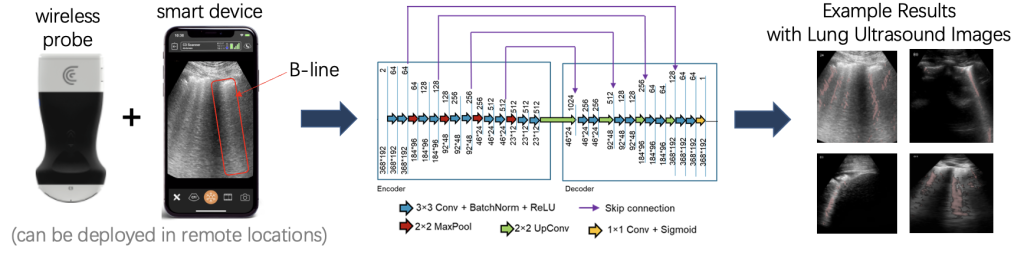
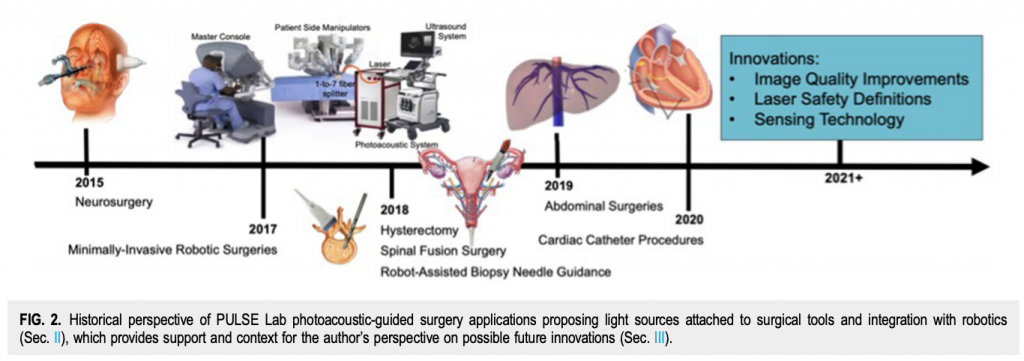
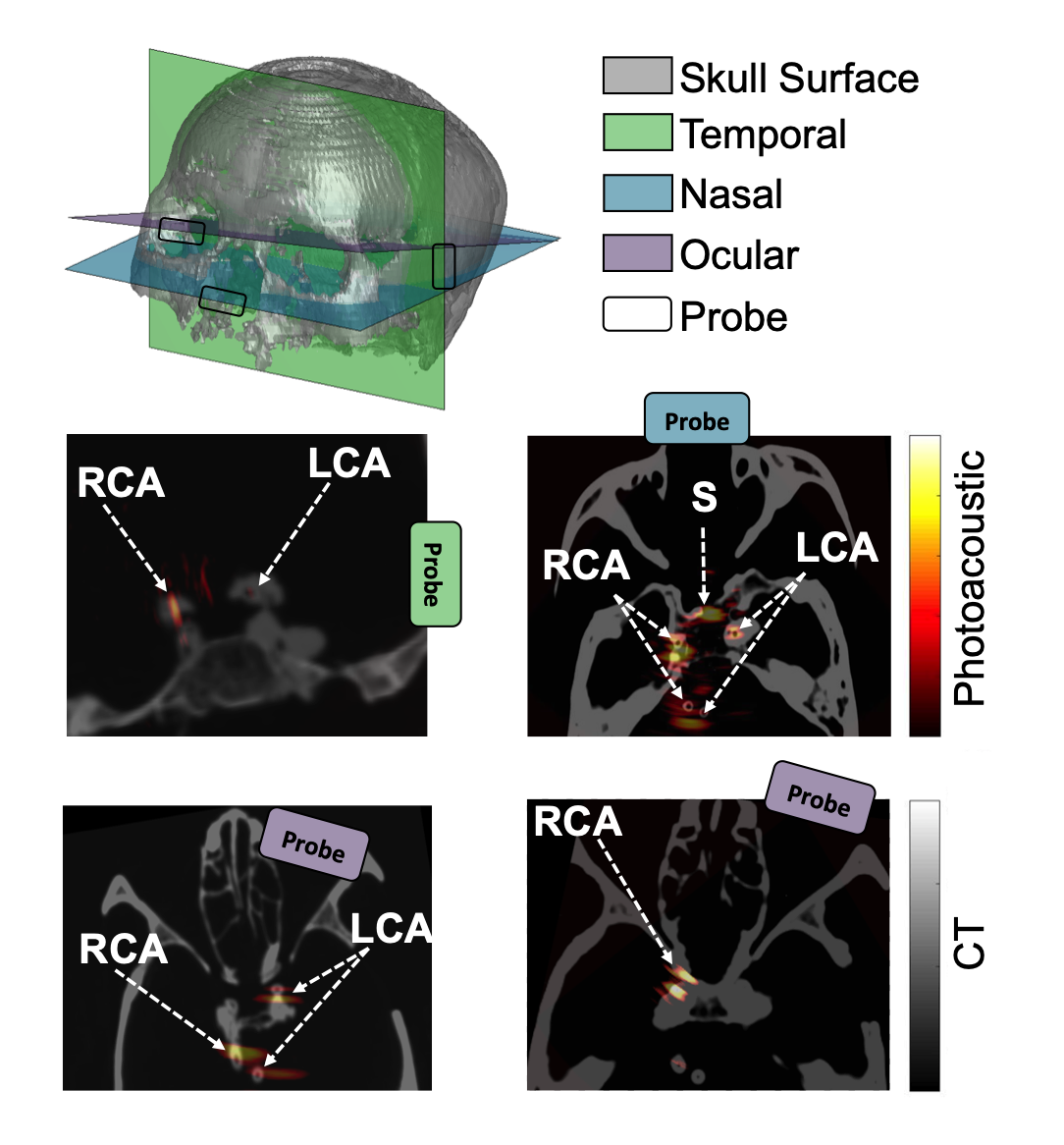
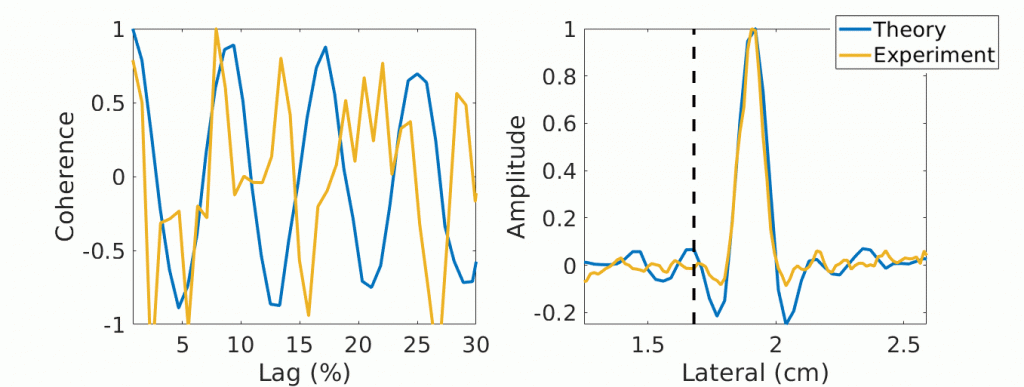
Welcome to five new PULSE Lab PhD students who joined us this fall:
PhD Student, ECE
M.S., Biomedical Engineering – Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, Lima, Peru
B.S., Electrical Engineering – Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, Lima, Peru
PhD Student, BME
B.S., Biomedical Engineering – Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, Lima, Peru
PhD Student, BME
B.S., Biomedical Engineering & Business – University of Rochester, NY, US
PhD Student, ECE
M.S.E., Biomedical Engineering – Johns Hopkins University
B.S., Biomedical Engineering – Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
PhD Student, ECE
M.S.E., Biomedical Engineering – Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MA, US
B.E., Biomedical Engineering – South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
Welcome Sebastian, Jose, Joselyn, Yanlin, and Yunlong! We are thrilled that you chose to pursue research with the PULSE Lab, and we wish you all the best on your PhD journey.
And, a belated welcome to Yun Zhang, who joined us as a Master’s student this past summer and is continuing her research with us this fall:
M.S.E. Student, ECE
Johns Hopkins University, Class of 2027
B.Sc., Software Engineering – University College Dublin
B.Eng., Software Engineering – Beijing University of Technology
Welcome Yun!