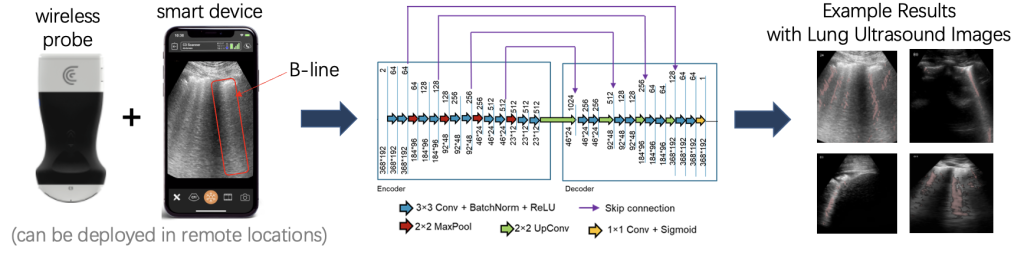
Congratulations to former PULSE Lab postdoc Lingyi Zhao! Her first-author journal paper entitled Detection of COVID-19 features in lung ultrasound images using deep neural networks was published in Communications Medicine, which is a Nature Publishing group journal). This paper is the first to demonstrate that simulations can be used to train deep neural networks to detect COVID-19 features in lung ultrasound images of patients. Therefore, DNNs trained with simulated and in vivo data are promising alternatives to training with only real or only simulated data when segmenting in vivo COVID-19 lung ultrasound features.
We offer public access (https://gitlab.com/pulselab/covid19) to the datasets and code described in the paper “Detection of COVID-19 features in lung ultrasound images using deep neural networks.” Communications Medicine, 2024. https://www.nature.com/articles/s43856-024-00463-5.
Access includes simulated B-mode images containing A-line, B-line, and consolidation features with paired ground truth segmentations, as well as our segmentation annotations of publicly available point of care ultrasound (POCUS) datasets (originating from https://github.com/jannisborn/covid19_ultrasound).
If you find our datasets and/or code useful, please cite the following references:
- L. Zhao, T.C. Fong, M.A.L. Bell, “Detection of COVID-19 features in lung ultrasound images using deep neural networks”, Communications Medicine, 2024. https://www.nature.com/articles/s43856-024-00463-5
- L. Zhao, M.A.L. Bell (2023). Code for the paper “Detection of COVID-19 features in lung ultrasound images using deep neural networks”. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10324042